Recently, radon has become a growing concern for homeowners, particularly those with floor heating systems. The way floor heating interacts with a home’s structure, heating system, and potential radon entry points can create unique risks. In this article, we dive into radon risk in homes with floor heating, explaining what it is, why it’s important, and how to handle it effectively.
By understanding these risks, you can better protect your indoor air quality and your family’s health. Whether you’re building new or upgrading an existing system, the right approach to radon control makes your warm floors safer, not riskier.

What is Radon And How It Enters Homes
Radon is a colorless, odorless radioactive gas that forms from the decay of uranium in the soil and rocks beneath your home. Being heavier than air, it tends to build up in lower areas, especially in basements or on ground-level floors. Radon enters homes through cracks in slabs, gaps around service pipes, or other openings in the foundation. Understanding how radon enters is essential when assessing radon risk in homes with floor heating, as floor heating systems can change the structure, floor layers, and airflow, potentially affecting how radon accumulates.
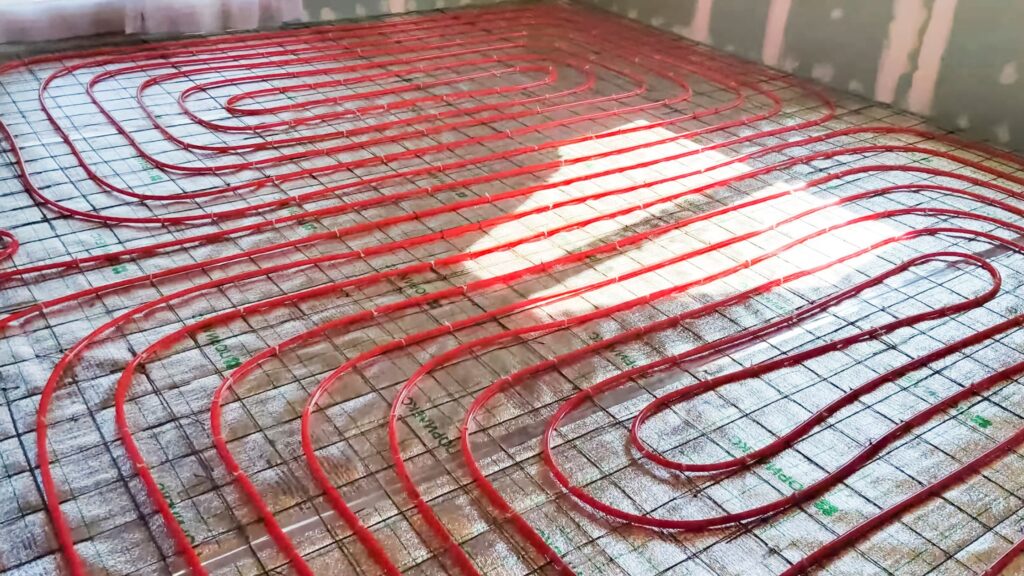
Radon Concerns in Homes with Floor Heating
Homes with underfloor heating (electric mats, hydronic tubes, or embedded panels) may face increased radon risk in homes with floor heating due to several factors:
- Floor heating systems use layers like insulation, screed, and heating tubes, which can create gaps between the floor and subfloor, allowing radon to enter.
- Heat from the floor can lower air pressure in living spaces, causing a “stack effect” that draws radon from beneath the floor.
- To improve energy efficiency, floor heating often seals the floor assembly, reducing ventilation and trapping radon longer under the surface.
- Retrofits to the slab or subfloor for heating may compromise previous radon-resistant measures, increasing the risk.
- Homes with low ventilation, typical of high-performance heating systems, can trap radon indoors, even in efficient setups.
Due to these risks, homeowners with floor-heated homes should prioritize radon testing and mitigation efforts. Learn more about Radon Mitigation for Underground Infrastructures.
Key Risk Factors Specific To Heated Floor Homes
To assess radon risk in homes with floor heating, consider the following factors:
- Contact with ground: Homes with heated floors directly on a slab or near soil/gravel are at higher risk. Radon can move through the soil and enter the heated slab interface.
- Floor heating retrofit: If the heating system was added after construction, ensure slab penetrations and floor joints were properly sealed to prevent radon entry.
- Insulation/ventilation trade-off: Modern floor heating systems often result in tightly sealed homes with reduced natural air exchange, increasing the potential for radon buildup.
- Existing cracks or gaps: Visible cracks in the floor, around the perimeter, or in heating system conduits may act as channels for radon to enter the living space.
- Winter usage patterns: Heated floors are often used when the home is closed up, increasing radon retention during colder months when ventilation is limited.
- Sub-slab pipes and conduits: These can unintentionally serve as pathways for radon unless properly sealed and ventilated.
By reviewing these indicators, you can determine if your floor heating system is contributing to radon risk in homes with floor heating.

Effective Testing and Early Detection Strategies
To manage radon risk in homes with floor heating, start with precise testing:
I. Short-term test: Conduct a 2–7 day test as an initial check, but keep in mind it may not capture seasonal variations in homes with floor heating.
II. Long-term test: Ideally, follow up with a 3-month to 1-year test to account for how floor heating cycles and ventilation patterns influence radon levels.
III. Test placement: Position the radon detector on the lowest lived-in level with floor heating, as this is typically where radon enters.
IV. Consider heating system activity: Don’t overlook times when the floor heating is active, as temperature and pressure changes can impact radon movement.
V. Action levels: If your test results exceed the recommended action level (e.g., 4 pCi/L in the U.S.), you must take mitigation steps.
VI. Ongoing risk: Even if the levels are below official action thresholds, continuing to reduce radon levels is always beneficial for health and safety.
Accurate testing is essential—without it, addressing radon risk in homes with floor heating is impossible.
Recommended Mitigation And Prevention Approaches
Once radon risk in homes with floor heating is identified, follow these mitigation steps:
- Seal cracks and penetrations: Close gaps around pipes, tubing, and the slab perimeter.
- Install sub-slab depressurization (SSD): Use a vent pipe and fan to pull soil gas out before it enters the home.
- Add a radon barrier when retrofitting: Place membrane/insulation under floor heating, leaving space for ventilation.
- Balance insulation and airflow: Don’t fully seal the subfloor; keep some ventilation to prevent radon buildup.
- Protect radon measures during changes: Ensure any floor-heating modifications still maintain radon control.
- Work with specialists: Use professionals familiar with both radon mitigation and radiant heating.
- Re-test after work: Check radon levels after mitigation and system changes to confirm they stay low.
Mitigating radon risk in homes with floor heating requires a comprehensive approach—sealing, airflow control, and regular monitoring.

Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding radon risk in homes with floor heating is crucial for homeowners who prioritize both comfort and health. While floor heating systems offer benefits, they can also create specific structural and airflow conditions that increase the risk of radon entry and buildup. By identifying risk factors, conducting proper testing, and implementing effective mitigation strategies—particularly with the help of experienced professionals—you can ensure a safe living environment. For expert testing and mitigation services, trust DSM Radon, where we provide tailored solutions to meet your home’s unique needs.