Cities grow fast, and they also stack more people closer to the ground, where soil gases move through tiny cracks and seams. Therefore, radon considerations for urban planning should live inside everyday planning decisions, not inside a late-stage checklist that teams remember only after complaints or failed inspections. Moreover, radon stays invisible and odorless, so communities cannot rely on “common sense” or symptoms to signal a problem. Consequently, planners protect residents, tenants, students, and workers when they pair zoning and redevelopment insight with consistent radon testing & mitigation and reliable radon mitigation services that deliver verified results.

Why Planners Must Treat Radon as Predictable
Radon rises from soil and rock, and buildings pull it indoors through pressure differences. Therefore, dense development and tighter envelopes can increase indoor accumulation when teams ignore soil gas pathways. Additionally, redevelopment can disturb soils and foundations, so older neighborhoods can face new radon patterns after major construction.
Consequently, radon considerations for urban planning help agencies reduce long-term risk by treating radon as a routine indoor-air variable, just like moisture control and ventilation strategy. Moreover, consistent testing, clear code triggers, and verified mitigation protect residents, simplify inspections, and strengthen public confidence across growing districts. Learn more aboutWhy Iowa Geology Produces High Radon.
Where Radon Enters in City Buildings
Radon enters through cracks, joints, sump pits, utility penetrations, and slab edges. Moreover, basements, crawlspaces, and split-level foundations create more contact points with soil gas. Additionally, mixed-use buildings often place mechanical rooms, shafts, and chases near slabs, so air movement can carry radon upward. Therefore, planners should push design teams to document entry points early, and they should also require radon testing & mitigation steps after any major foundation work. Furthermore, teams should seal high-risk penetrations, keep clear vent routes, and add radon-ready rough-ins during construction, so future mitigation installs stay faster, cleaner, and less disruptive for occupants.
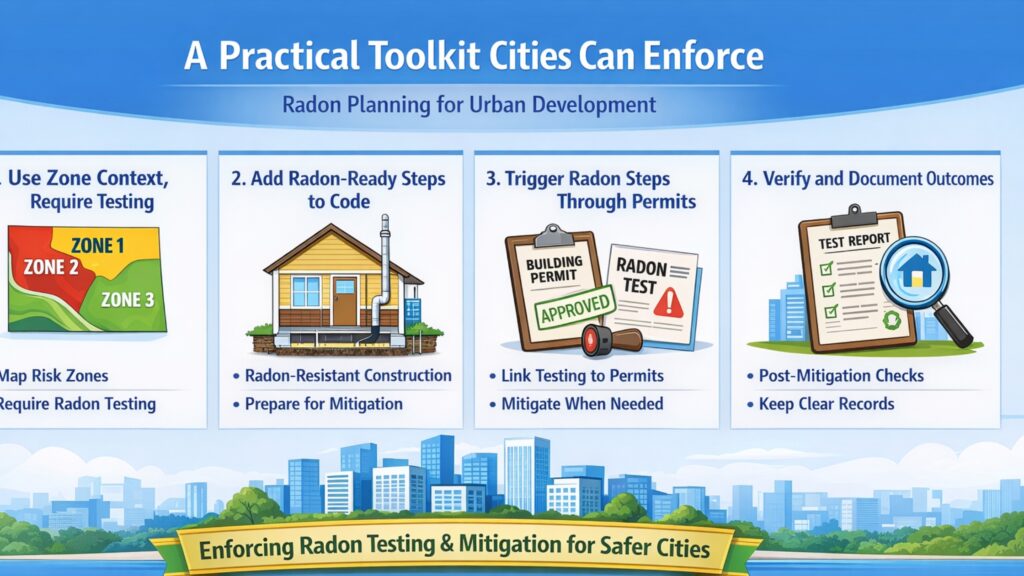
A Practical Toolkit Cities Can Enforce
Cities often win when they standardize a few strong levers. Therefore, radon considerations for urban planning can focus on mapping, codes, permitting, and verification while keeping workflows simple.
1) Use Zone Context, Require Testing
EPA-style zone context can guide outreach and prioritization. However, radon varies a lot, so testing should drive decisions for each building. Therefore, agencies should require radon testing & mitigation plans for ground-contact occupancies, and they should also track results to refine local policy.
2) Add Radon-Ready Steps to Code
Cities can encourage radon-resistant features during new builds and major renovations. Moreover, radon-ready paths reduce disruption because teams plan routing, sealing, and venting early. Therefore, codes can prompt slab sealing, sub-slab prep, and clear vent pathways that support radon mitigation services.
3) Trigger Radon Steps Through Permits
Permits can create the “when” that builders follow. Consequently, a permit workflow can require pre-occupancy testing for certain use types, and it can also require mitigation when results demand action. Therefore, radon testing & mitigation becomes a predictable milestone instead of a vague suggestion.
4) Verify and Document Outcomes
Verification keeps policy honest. Therefore, cities should require post-mitigation testing documentation and simple records that inspectors can review. Additionally, clear records reduce disputes during leasing, resale, and occupancy changes, and they build public trust through consistent enforcement across neighborhoods.
Ultimately, these levers enforce radon considerations for urban planning through documented radon testing and radon mitigation services.
Radon Mitigation Services
Cities expand fast, so planners need repeatable protection that follows every project. Therefore, radon mitigation services turn radon testing & mitigation into verified indoor safety across building types.
- Source control: Radon mitigation services manage soil gas below the building, so less radon enters indoor spaces.
- Clear next steps: Teams connect radon testing & mitigation, so elevated results trigger action without delay.
- Verified results: Providers retest after mitigation and document outcomes, which support inspections and records.
- High-occupancy fit: Schools, offices, and apartments benefit because radon mitigation services protect many people at once.
This approach keeps radon considerations for urban planning practical, enforceable, and measurable as cities grow.
A City-Ready Workflow For Radon Testing and Mitigation
A city workflow should feel simple for builders and protective for occupants. Therefore, you can structure a practical sequence that repeats across projects:
- Planning staff require a brief radon note with milestones.
- Teams test on schedule using one consistent placement protocol.
- When levels run high, start mitigation fast with low disruption.
- Teams retest, document results, and file records for pattern tracking.
Moreover, this repeatable workflow replaces guesswork with verified protection through radon testing & mitigation and radon mitigation services.
Implementation Roadmap For Planning Departments
A policy can start small and still protect people well. Therefore, radon considerations for urban planning can roll out in phases, starting with high-risk zones, then expanding citywide as data improves.
- Standard language and training: You should publish a one-page radon workflow, and you should train plan reviewers on the trigger points for radon testing & mitigation.
- Priority-building program: You should launch a focused cycle for schools and public facilities, and you should also add multi-family triggers that match occupancy risk.
- Reporting and continuous improvement: Track compliance, document outcomes, and refine requirements. Moreover, keep access clear for radon mitigation services.
Moreover, these phases scale radon considerations for urban planning through consistent radon testing & mitigation and clear access to radon mitigation services.

Conclusion
When you embed radon considerations for urban planning into everyday permitting and verification, you protect more people while reducing uncertainty for builders and inspectors. Moreover, when cities align radon testing & mitigation with dependable radon mitigation services, they create healthier indoor environments across neighborhoods, schools, workplaces, and multi-family housing. For comprehensive testing, mitigation, and verification support designed for real urban conditions, partner with DSM Radon —a trusted local provider serving the Des Moines metro with professional systems that support compliance, clear documentation, and long-term indoor safety.





