Radon, a naturally occurring radioactive gas, silently infiltrates homes and poses significant health risks, including lung cancer. As a homeowner, understanding radon sources is crucial to protect your family and maintain a safe living environment. This article explores how radon enters your home and offers proven solutions to mitigate its dangers. By learning how radon moves through soil and structures, you can take targeted action to block its entry. Awareness and timely testing are the first steps toward lasting protection and peace of mind.

What is Radon?
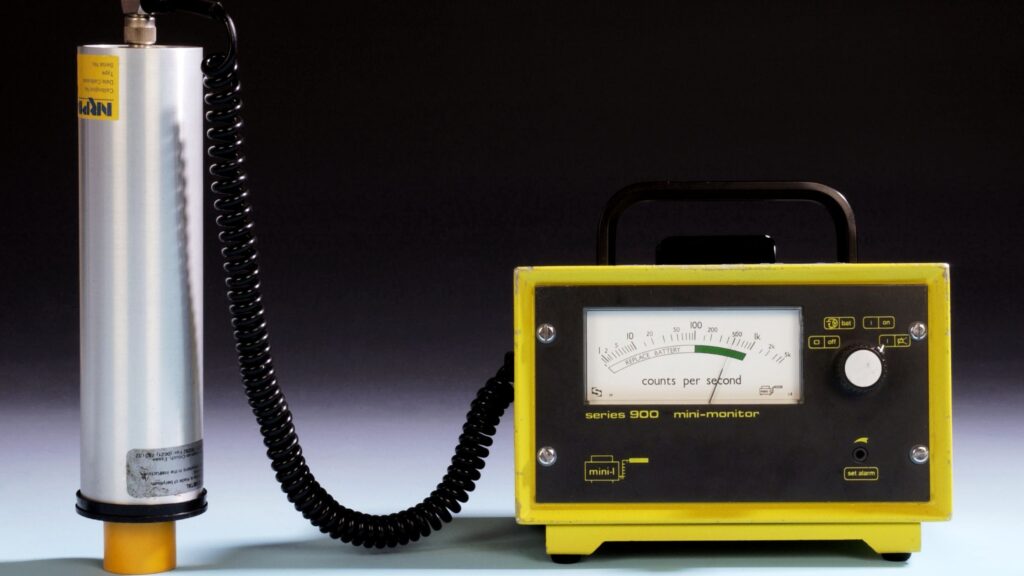
Radon is a radioactive gas that forms naturally when uranium, thorium, and radium in soil, rocks, and water decay. It is colorless, odorless, and tasteless, making it undetectable without proper testing. In confined spaces, particularly in basements and ground-level areas, radon can accumulate to harmful levels, significantly increasing health risks.
Radon exposure is the second leading cause of lung cancer, particularly for non-smokers. Long-term exposure to elevated radon levels can lead to serious respiratory issues, making early detection and mitigation crucial for health. Even small amounts over time can accumulate and cause lasting harm. Regular testing is the only way to detect and control this invisible threat.
How Radon Enters Your Home: Key Sources
Radon can enter your home through various pathways, including soil, foundation cracks, well water, and building materials. Understanding these sources is crucial for effective mitigation and protecting your health.
1. Soil and Bedrock
Radon primarily originates from the ground beneath your home. As uranium and radium decay in soil and rocks, they release radon gas. The concentration varies based on your location, with some regions having higher radon levels due to geological factors.
2. Foundation Cracks and Gaps
Cracks in the foundation or gaps around pipes provide easy entry points for radon. These openings allow gas to seep in from the ground below, often concentrating in basements and lower levels where ventilation is poor.
3. Well Water
In areas where water sources are drawn from wells, radon can also be present. When water containing radon is used in your home, it can release the gas into the air, further elevating indoor radon levels.
4. Building Materials
Some materials used in construction, such as granite or concrete, can contain small amounts of uranium, contributing to radon exposure. However, these materials alone typically don’t account for high levels of radon.
Understanding how radon enters your home is key to prevention. Identifying its sources helps you take action to reduce exposure and keep your home safe. Learn more about Where Is Radon Found.
Health Risks of Long-Term Radon Exposure
Long-term exposure to elevated radon levels is a significant health risk, with radon being the second leading cause of lung cancer, just after smoking. When inhaled, radon’s radioactive particles become trapped in the lungs, where they emit radiation that can damage lung tissue. This damage over time increases the likelihood of developing lung cancer.
Even non-smokers are at an elevated risk of lung cancer from radon exposure, as the gas can cause similar harmful effects on lung cells. Prolonged radon exposure can also lead to respiratory diseases like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and emphysema, which impair lung function and overall health.

Radon Sources in Commercial and Industrial Spaces
Radon exposure is not limited to residential buildings—it also poses significant risks in commercial and industrial environments.
a) Geological Impact
Commercial and industrial properties located in areas with uranium-rich soil or rock formations are more likely to experience elevated radon levels. These properties need special attention due to their proximity to geological factors that contribute to radon seepage.
b) Underground Workspaces
Underground commercial spaces, such as basements, storage areas, and tunnels, are especially susceptible to high radon concentrations. Due to limited ventilation and proximity to the soil, these areas pose a higher risk of radon buildup.
c) Warehouses & Manufacturing
Warehouses and manufacturing facilities, particularly those located near mining or construction zones, may face radon issues. Workers in these environments could be exposed to higher radon levels over long periods, increasing the risk of health complications.
d) Mitigation Regulations
The commercial sector is subject to specific regulations regarding radon mitigation, particularly in high-risk areas. Businesses must comply with local and national radon standards to ensure the safety of workers and customers, including regular testing and installation of mitigation systems.
e) HVAC and Ventilation Systems
Poorly maintained HVAC systems can trap radon instead of dispersing it. Efficient ventilation helps dilute radon and circulate fresh air. Regular HVAC inspections and upkeep ensure proper airflow and reduce radon buildup in commercial spaces.
By recognizing these radon sources, commercial and industrial facility managers can take proactive steps to monitor, test, and mitigate risks.
Proven Ways to Reduce Radon from Indoor Sources
Simple steps can greatly lower radon levels and keep your indoor air safe.
- Install a Mitigation System: A sub-slab system removes radon from beneath the foundation and vents it outside.
- Seal Entry Points: Close cracks and gaps in floors, walls, and pipes to limit radon intrusion.
- Improve Ventilation: Increase airflow with fans or vents to dilute indoor radon levels.
- Test Regularly: Recheck radon every two years or after renovations to maintain safety.
Consistent testing and maintenance keep your home protected, ensuring long-term safety and peace of mind.
Conclusion
Radon is a silent health threat, but its risks are preventable. Regular testing and mitigation can reduce radon levels and safeguard your family’s health. If you’re concerned about radon in your home, professional services like those offered by DSM Radon can help ensure a radon-free environment. Act today to protect your home and health. Early detection is the key to prevention—don’t wait for symptoms to appear. With expert guidance and proper systems, you can breathe easier knowing your indoor air is safe.





