Radon is a radioactive gas that comes from the breakdown of uranium in soil. It can be harmful to health if it is found inside buildings. People who work with radon need to know about its physical properties. One of the important properties is the radon boiling point. This is the temperature at which radon changes from liquid to gas or from gas to liquid. This article will explain what the radon boiling point is. It will also show why it matters for finding and reducing radon.

Table of Contents
- What is Radon?
- Physical Properties of Radon
- What is the Radon Boiling Point?
- Why the Radon Boiling Point Matters
- Radon in Indoor Environments
- Radon Detection and Mitigation Techniques
- FAQ
- Conclusion
1. What is Radon?
Radon is a gas that you can’t see, smell, or taste. It forms naturally when uranium breaks down in the soil, rocks, and water. Radon is a noble gas, which means it doesn’t mix or react much with other things. But even though it’s not easy to notice, radon can build up inside closed areas like homes. Breathing in high levels of radon for a long time can be very harmful and may lead to lung cancer.
To keep people safe, it’s important to understand how radon acts. Learning about its properties—like the radon boiling point—can help us control and reduce its risks
2. Physical Properties of Radon
Radon is part of a group called noble gases on the periodic table. It is heavier than air and has special features that affect how it moves and gathers inside buildings. Some important facts about radon are:
- Atomic number: 86
- Atomic mass: 222 u
- State at room temperature: Gas
- Density: About 9.73 grams per liter (which is around 7.5 times heavier than air)
One important feature is the radon boiling point. This is the temperature where radon changes from a liquid to a gas or the other way around. Knowing this helps us understand how radon behaves in different temperatures.
3. What is the Radon Boiling Point?
The radon boiling point is the temperature when radon turns from a liquid into a gas at normal air pressure. For radon, this happens at about -61.7°C (-79.1°F). Because this temperature is very low, radon usually stays in gas form in everyday conditions. This means it can easily move and spread through the air.
Radon’s boiling point is higher than lighter gases like helium or neon, but lower than heavier gases like xenon. This boiling point depends on radon’s weight and how its atoms stick together. These factors affect how radon behaves both in nature and inside buildings. Learn more about Radon gas.

4. Why the Radon Boiling Point Matters
You might ask why the radon boiling point is important. It’s not just a science fact—it actually helps in real-world situations:
A.Detection Tools:
Because radon stays a gas at normal temperatures, experts can make tools that find radon gas easily. They don’t have to worry about it turning into a liquid.
B.Mitigation Systems:
In homes, radon stays a gas, so systems are made to stop it from building up. This includes adding fans, vents, and sealing cracks to keep the gas from getting inside.
C.Storage and Testing:
In labs, knowing the boiling point helps people store and test radon properly. It helps them measure radon levels more accurately.
That’s why people who work with radon use this knowledge to find better and safer ways to protect homes and health.
5. Radon in Indoor Environments
Radon gas usually gets into buildings through cracks in the floors, walls, and foundations. It can also come in through well water. Because radon is heavier than air, it tends to build up in basements or lower parts of a home, making the levels inside go up.
The radon boiling point also plays a small but important part. Since radon stays a gas at normal home temperatures, it can easily move through the air and small gaps. That’s why it’s important to check and measure radon levels often.
Changes in temperature can also affect how radon behaves. In colder months, warm air from inside the house rises and escapes, which pulls more radon in from the ground. This can make radon levels even higher indoors.
6.Radon Detection and Mitigation Techniques
Experts use different methods to find and lower radon levels.
- Radon Detectors: Tools like charcoal canisters, alpha track detectors, and electronic monitors are made to detect radon gas. Since radon stays a gas at normal temperatures, these tools can measure it easily.
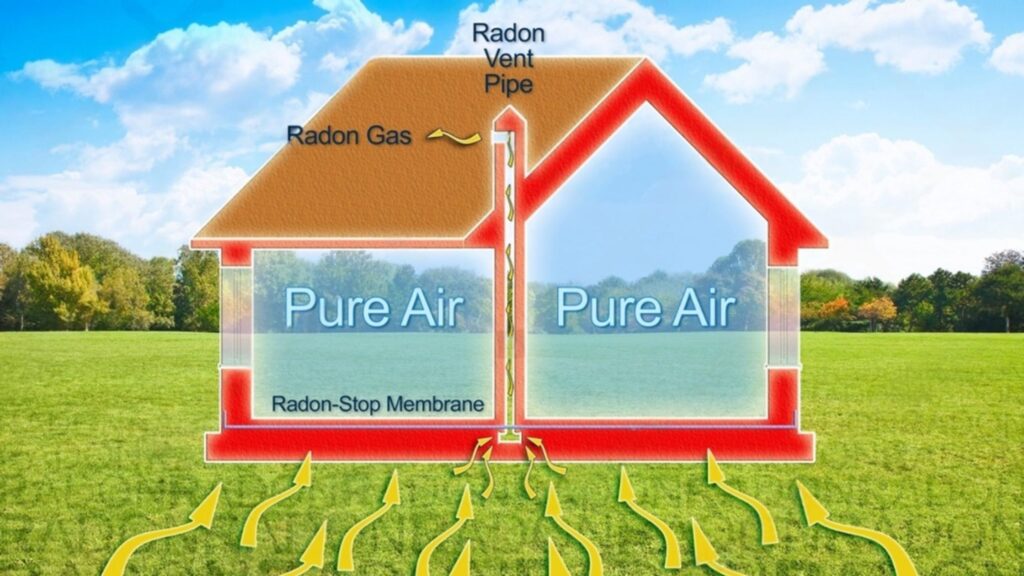
- Mitigation Systems: Systems like sub-slab depressurization remove radon gas from under the home before it gets inside. Because radon stays in gas form, these systems can vent it out effectively.
- Sealing and Ventilation: Sealing cracks and improving airflow helps stop radon from building up. Since radon gas can pass through tiny spaces, sealing is very important.
In short, understanding the radon boiling point helps experts design better ways to detect and remove radon from indoor air.
7.FAQ
A.How does a radon mitigation system work?
It uses fans and pipes to draw radon from the ground and release it outside.
B.Is it safe to run all the time?
Yes, it’s designed to run continuously and safely.
C.How long does installation take?
Most systems are installed in one day.
8.Conclusion
It is very important to know about radon boiling point. It affects how radon acts both outdoors and inside buildings. Since radon stays at normal temperature, it can easily enter homes and offices. This makes it a serious health risk.
Knowing the radon boiling point helps the experts detect and reduce radon more effectively. For expert help, contact DSM Radon. They offer radon testing, removal, and advice. Their advanced systems are designed to keep your indoor air safe and radon-free.





