Radon is a naturally occurring radioactive gas that has drawn concern because of its health hazards. Invisible and without smell or taste, it can build up inside buildings and potentially endanger human health. The radon element is produced by the decay of uranium and thorium in the Earth’s crust. Over time, it can seep into buildings through cracks in floors and walls, where it may build up to dangerous levels.
This article will explore the radon element, its properties, sources, health risks, and how you can detect and mitigate its presence in your home. We’ll cover various aspects to ensure you have a thorough understanding of this harmful gas and how to protect your family from its potential dangers.

Table of Contents
- What is Radon?
- How Radon Forms and Its Sources
- Health Risks Associated with Radon Exposure
- Radon Detection Methods
- Mitigation Techniques for Radon
- Radon in the Environment
- How to Reduce Radon Levels in Your Home
- Conclusion
What is Radon?
The radon element is a radioactive gas that occurs naturally during the decay of uranium and thorium in rocks and soil. It is part of the noble gases group, which means it doesn’t react with other elements easily. However, its radioactive properties make it potentially harmful, especially when concentrated indoors.
Unlike other gases, radon can build up in closed spaces such as homes and buildings, leading to high concentrations. Understanding the behavior of radon is essential for preventing its accumulation and mitigating its risks. Learn more about radon here.
How Radon Forms and Its Sources
Radon is formed as a result of the breakdown of uranium, which is found in rocks, soil, and water. Over millions of years, uranium decays into radon gas, which then escapes from the Earth’s crust and rises through cracks and fissures. They can enter homes and buildings through various entry points, such as foundations, sump pits, and floor cracks.
Certain areas are more prone to higher radon concentrations due to the geological composition of the land. Areas with higher concentrations of uranium in the soil or rock are more likely to have higher radon levels.
Risks Associated with Radon Exposure
Exposure to high levels of radon is linked to serious health risks, primarily lung cancer. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), radon exposure is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking. When radon gas is inhaled, radioactive particles can get trapped in the lungs, causing damage to the lung tissue over time.
Long-term exposure to radon can lead to chronic health problems, and people living in homes with high radon levels are at increased risk. This is particularly dangerous for smokers, as the combination of radon exposure and smoking significantly increases the risk of lung cancer.
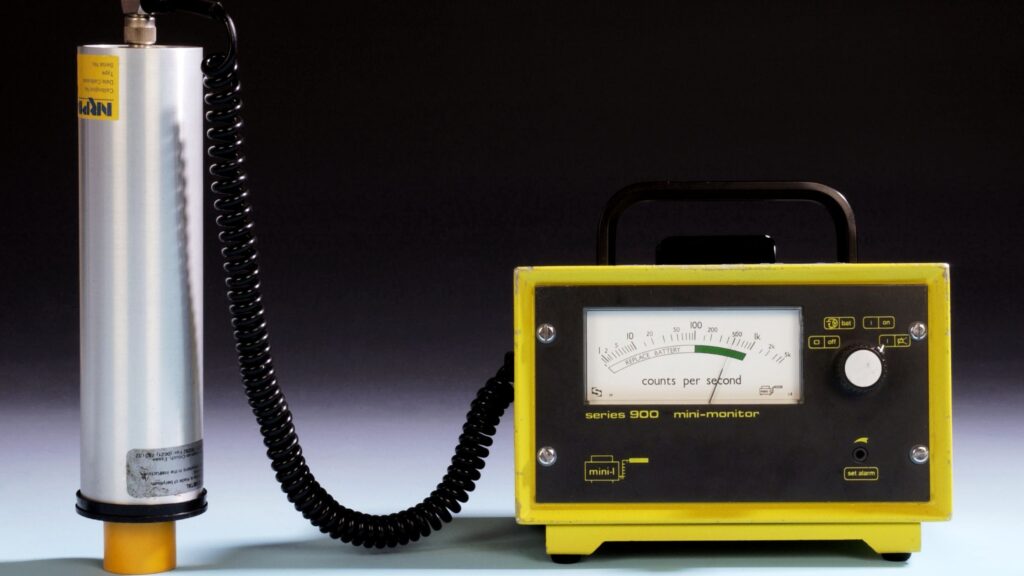
Radon Detection Methods
Detecting radon in your home is the first step toward protecting your health. Fortunately, there are several methods available to check for radon presence.
- Short-Term Testing
Short-term tests are simple and quick ways to measure radon levels in your home. These tests typically last between two and seven days and can be done with a kit purchased online or from a local hardware store.
- Long-Term Testing
Long-term tests, on the other hand, measure radon levels over a period of 90 days or more. These tests provide a more accurate assessment of the average radon concentration in your home.
- Professional Radon Testing
For the most reliable results, you can hire a professional radon tester who can assess radon levels in your home using specialized equipment.

Mitigation Techniques for Radon
If testing reveals elevated radon levels in your home, it’s essential to take steps to reduce it. Several mitigation techniques are available, depending on your home’s design and radon levels.
I. Radon Ventilation Systems
One of the most effective methods for radon mitigation is installing a radon ventilation system. This system involves a vent pipe and fan that directs radon gas from beneath the building to the outside air.
II. Sealing Cracks and Gaps
Sealing cracks and gaps in the foundation can prevent radon from entering your home. Although this method alone may not be enough to reduce radon levels significantly, it is an important part of the overall mitigation process.
III. Soil Depressurization
Soil depressurization involves creating a negative pressure zone beneath the house to prevent radon from entering. This technique is often combined with other methods like ventilation systems for better results.
Radon in the Environment
Radon is not only present in homes but also in natural environments such as caves, mines, and even some outdoor areas. While outdoor concentrations of radon are typically low and pose no immediate risk, it can accumulate in poorly ventilated areas.
In some cases, certain regions have a higher natural occurrence of radon due to the geological makeup of the land. For instance, granite-rich areas are known to have higher radon levels compared to other types of rock.
How to Reduce Radon Levels in Your Home
Reducing radon levels in your home is crucial for safeguarding your health. Here are some simple steps you can take:
- Test your home regularly: Regular testing helps you monitor radon levels and take action if they rise.
- Seal entry points: Sealing cracks and gaps around the foundation, windows, and doors can help minimize radon infiltration.
- Install a radon mitigation system: This is the most effective method for reducing radon levels in homes.
- Ventilate your home: Ensuring proper ventilation by opening windows or using fans can help dissipate radon gas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the radon element is a significant concern for homeowners due to its potential health risks, particularly lung cancer. Fortunately, through proper detection, mitigation techniques, and regular testing, you can reduce radon levels in your home and protect your family.
For more information and expert help on detecting and mitigating radon, you can visit DSM Radon, where they offer professional radon testing and mitigation services.
By understanding the properties and risks of radon, you can take proactive steps to ensure your home remains safe and free from this hazardous gas.




